Sustainable Construction: Techniques and Strategies for Green Architecture
Sustainability in civil construction is a topic of extreme importance nowadays, especially due to the climate changes we are facing. In this context, sustainable construction becomes fundamental to mitigate environmental impacts and promote the use of more responsible practices.
The civil construction industry is responsible for excessive consumption of natural resources and approximately 39% of global greenhouse gas emissions, according to the 2018 Global Alliance for Buildings and Construction (GABC) report, which directly contributes to global warming and environmental degradation.
Why Is Sustainable Construction Urgent?
Sustainable constructions are not just a trend; they are a necessary revolution for the civil construction industry.
It is essential to adopt practices for sustainable construction, aiming to minimise environmental impacts and promote the preservation of natural resources. Fortunately, there are various techniques and strategies that can be applied during the construction process, ensuring energy efficiency, waste reduction and the use of sustainable materials.
1. Sustainable Materials in Civil Construction
Reuse and Recycling of Materials
One of the main techniques for sustainable constructions is the reuse, recycling and use of local materials. This approach is increasingly important to minimise the environmental impact of buildings.
Reuse of Materials
An effective way to reduce waste and demand for new materials is to reuse those that are already available. Sustainable materials such as wood, glass, metal and even bricks can be repurposed in new constructions or renovations. Besides minimising the extraction of natural resources, reuse can also add a unique and historical charm to green architecture projects.
Recycling of Materials
Recycling is another important aspect of sustainable construction. Sustainable materials include soil cement, recycled concrete, alternative woods, ecological tiles, plastic, cardboard and concrete that can be recycled and transformed into new products for use in construction.
Innovative and Sustainable Materials
According to recent research on sustainable materials in civil construction, these stand out:
- Bioconcrete: Self-repairing material that uses bacteria
- Adobe Brick: Traditional sustainable building material made of earth, sand and natural fibres that provides excellent thermal insulation without requiring firing
- Bamboo: Renewable material with excellent resistance
- Clay Grout: Can replace conventional cement with significant results and excellent finishing
- Ecological Tiles: Made from natural fibres or recycled resources
Use of Local Materials
By using local materials, we reduce the need for transport over long distances, contributing to the reduction of carbon emissions. Additionally, the use of local materials helps to promote the local economy and values the resources available in the region. Stones, woods, ceramics and other regional materials can confer a sense of identity and belonging to sustainable architecture projects.
2. Bioclimatic Design Strategies
For Hot Climates
Thermal comfort is an important aspect to consider when designing buildings in hot climates. Through the use of bioclimatic design strategies, it is possible to minimise the need for active cooling systems, thereby reducing energy consumption and environmental impacts.
Effective strategies include:
- Thermal Insulation: Use high-quality insulating materials in walls, roofs and floors to prevent excessive heat transfer to the interior of the building.
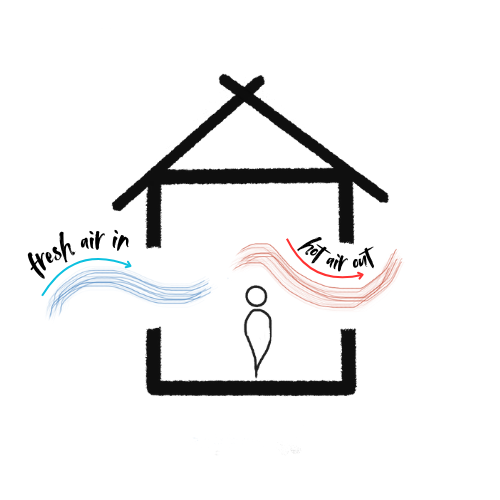
- Natural Ventilation: Design the building to allow the entry of fresh air and natural air circulation. This can be achieved through the use of strategically positioned windows, ventilation openings and ceiling fans.
- Solar Protection: Use shading elements, such as brise-soleils, blinds or vegetation, to block direct solar radiation and reduce heat gain inside the building.
- Appropriate Construction Materials: Choose construction materials with appropriate thermal properties, such as reflective tiles, which help reduce heat absorption.
- Layout Planning: Consider the orientation of the building and the positioning of its openings to efficiently take advantage of sunlight and natural ventilation.
For Cold Climates
Bioclimatic design is an efficient approach to achieve thermal comfort in cold climates without excessive energy use. This type of design is based on strategies that utilise available natural resources.
Strategies for cold climates:
- Orientation and Layout: Position the building to capture direct sunlight during the day, especially in areas of greater use.
- Insulating Glass: Use double or triple glazing with thermal insulation to reduce heat loss through windows.
- High Performance Materials: Use sustainable construction materials with high thermal insulation capacity, such as concrete block walls with internal or external insulation.
- Radiant Floors: Systems that heat the environment from the floor, providing uniform heat distribution.
- Controlled Ventilation: Implement systems such as air heat exchangers to efficiently renew air.
3. Energy Efficiency Strategies
For 2024, the expectation is that the civil construction sector will advance in sustainable projects, with trends and technologies associated with the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Main Strategies:
- Advanced Thermal Insulation: Use efficient insulating materials in walls, ceilings and floors to maintain stable temperature and reduce the need for climate control.
- Efficient Windows: Install high-quality windows with double glazing and good sealing to minimise thermal losses.
- LED and Smart Lighting: Replace conventional lamps with LED lights, using motion sensors or smart lighting systems.
- Efficient Equipment: Opt for high energy efficiency appliances and HVAC systems.
- Renewable Energies: In Brazil, technologies such as solar panels, green roofs and home automation systems are gaining prominence, allowing buildings to reduce energy consumption and optimise resource use.
- Smart Energy Management: Implement control and automation systems that monitor and adjust energy consumption in real time.
4. Efficient Water Resource Management
In sustainable construction, it is essential to adopt measures for efficient water use. An effective strategy is rainwater harvesting, which allows the use of a natural resource and reduces potable water consumption.
Water Strategies:
- Rainwater Collection: Collection system through gutters and directing to appropriate reservoirs
- Water-Saving Devices: Taps with presence sensors and showers with flow restrictors
- Greywater Reuse: Treatment and reuse of water from washbasins and showers
- User Awareness: Educational campaigns on responsible water use
Green roofs are sustainable structures that contribute to water management in addition to providing thermal insulation and improving air quality.
5. Green Architecture and Urban Sustainability
Principles of Green Architecture
Green architecture is not new. The principles behind it are as old as human civilisation. Green buildings are designed to:
- Reduce environmental impact
- Save energy
- Use sustainable materials
- Generate their own energy
Emerging Technologies
Bioconcrete, bioplastic, ecogranite, solar panel, adobe brick and recycled blanket are some of the sustainable materials that have been gaining more and more space in the sector.
Economic Benefits of Sustainable Construction
Financial Advantages:
- Reduction of 20-50% in energy consumption
- Savings of 30-50% in water consumption
- Property appreciation of 10-20%
- Lower long-term maintenance cost
- Tax incentives and special financing
Return on Investment:
The initial investment in sustainable materials and green technologies usually pays for itself in 3 to 7 years through operational savings, in addition to adding significant value to the property.
Trends for 2024-2025
Highlighted Innovations:
- Sustainable Modular Construction
- Artificial Intelligence in Energy Management
- Biocompatible Materials
- Distributed Energy Systems
- Integrated Urban Agriculture
Public Policies
Research analyses the existing public policies in Brazil that promote sustainable civil construction, identifying main challenges and opportunities. The Brazilian government has implemented various initiatives to encourage sustainability in civil construction.
Conclusion: The Future is Sustainable
Building sustainably is a responsibility for all of us. By adopting reuse, recycling and use of local materials, in addition to bioclimatic design and energy efficiency strategies, we can contribute to environmental preservation and create more efficient and conscious buildings.
Sustainable construction represents not only an environmental necessity but also an economic opportunity. With Brazil standing out in the world scenario of green architecture, professionals who master these techniques and strategies will be at the forefront of the sector.
The strategies presented – from the use of sustainable materials to the implementation of energy efficiency technologies – are investments in the future of our planet and in the quality of life of future generations.
To delve even deeper into the topic, check out our other posts about 5 benefits of sustainable construction and continue following the blog for more content on green architecture and sustainability in civil construction.


Wow, this post has given me useful info and answered some of my questions. I hope to give something back and aid others like you helped me. Feel free to surf my website Webemail24 about Print on Demand Services.
It appears that you know a lot about this topic. I expect to learn more from your upcoming updates. Of course, you are very much welcomed to my website Seoranko about SEO.
Superb and well-thought-out content! If you need some information about Podcasting, then have a look at ZQ3